- Joined
- Feb 2, 2011
- Messages
- 2,093
NEW RELEASES FOR APRIL 2022
THE ANCIENTS COLLECTION
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF ANCIENT ROME
THE CARTHAGINIANS
Ancient Carthage was a Phoenician state founded in 814BC. The Carthaginian Empire was to extend over much of the coast of Northwest Africa as well as substantial parts of coastal Iberia and the islands of the western Mediterranean sea.
At its height, the city state served as a major hub of trade, which brought it into conflict with the Greeks in Sicily, and with the Roman Republic, which led to a series of conflicts known as the Punic Wars.
CARTHAGINIAN WARSHIP
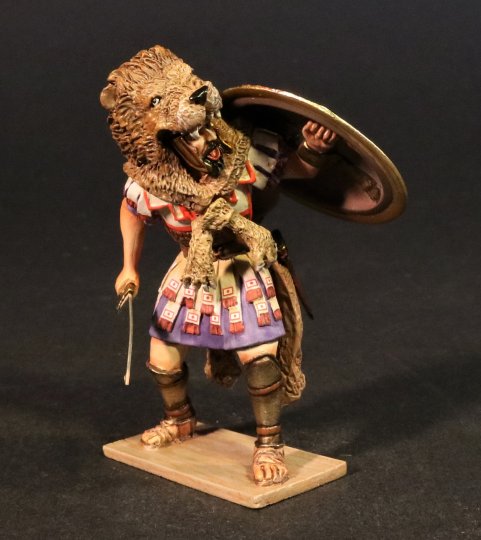

BTCT-06
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF ANCIENT ROME,
THE CARTHAGINIANS,
CARTHAGINIAN OFFICER.
(1 pc)
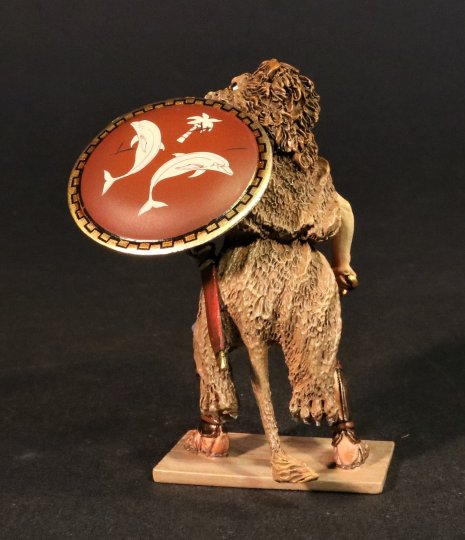


BTCT-07
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF ANCIENT ROME,
THE CARTHAGINIANS,
CARTHAGINIAN STANDARD BEARER.
(1 pc)

The military of Carthage was one of the largest military forces in the ancient world. Although the navy was always Carthage’s main force, the army acquired a key role in the spread of Carthaginian power.
With its Phoenician origins, Carthage already had a long history as a seafaring people. This was helped in that the navy was a permanently manned force, whilst the army would be enlisted only for a particular campaign and then demobilized.
Therefore it was easier to understand how the Carthaginian army was a Combined arms force, which comprised light and heavy infantry, skirmishers, light and heavy cavalry, as well as elephants.
The supreme command of the military was initially held by the civilian “Suffetes” until the third century. Thereafter, professional military generals were appointed directly by the Carthaginian Senate.
Whilst the navy was mainly manned by citizens, the army was composed almost exclusively of foreign mercenary units, particularly Libyans, Numidians, Iberians, Gauls and Greeks.
Only when the city of Carthage itself was threatened would citizens be conscripted into infantry service.
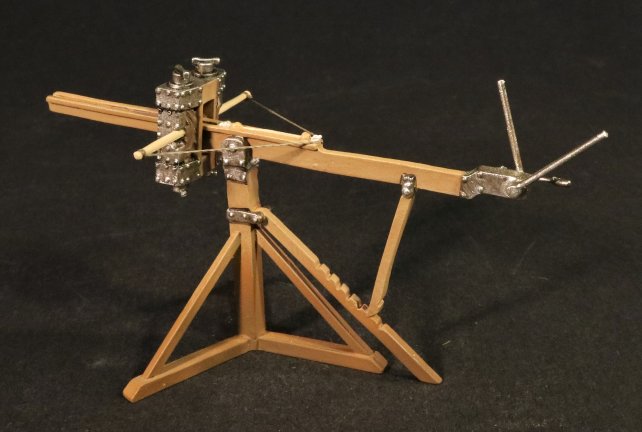
BTCT-12
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF ANCIENT ROME,
THE CARTHAGINIANS,
SCORPION.
(1 pc)
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF GREECE AND MACEDONIA
THE SCYTHIANS
The Scythians were an ancient nomadic people living primarily in the region known as Scythia, which today comprises the Eurasian steppes of Kazakhstan, the Russian Steppes of the Siberian, Ural, Volga and Southern regions , and eastern Ukraine.

The Scythians were a warlike people. When engaged at war, almost the entire adult population including a large number of women, participated in battles. The Athenian historian Thucydides noted that no people in either Europe or Asia could resist the Scythians without outside aid.
The scythians were particularly known for their equestrian skills, and their use of the composite bow shot from horseback. With great mobility, the Scythians could absorb the attacks of more cumbersome foot and cavalry, just retreating into the steppes. Such tactics wore down their enemies, making them easier to defeat.
Due to their notorious reputation as aggressive warriors they frequently gained employment as mercenaries.
By the late 6[SUP]th[/SUP] Century BC, the Persian Achaemenid King Darius The Great had built Persia into becoming the most powerful empire in the world, stretching from Egypt to India.
Planning an invasion of Greece, Darius first sought to secure his northern flank against the Scythians.
Darius sent a fleet of over 600 ships into Scythian territory. The army captured several Scythian Nobles. The army according to Herodotus numbered 700,000 men.
Unable to withstand the direct force of the Persian army, the Scythians adopted a scorched earth strategy, while simultaneously harassing the extensive Persian supply lines. The Persians suffered heavy losses and only proceeded as far as the Sea of Azov.
Darius and his army eventually retreated across the Danube back into Persia, and the Scythians thereafter earned a reputation of invincibility among its neighboring peoples.
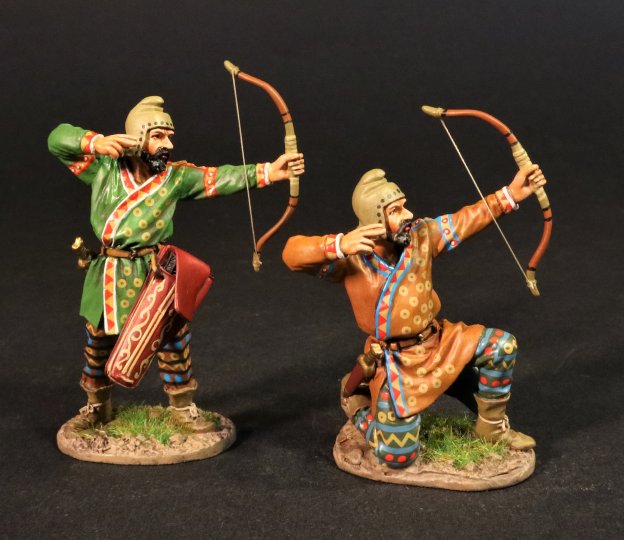

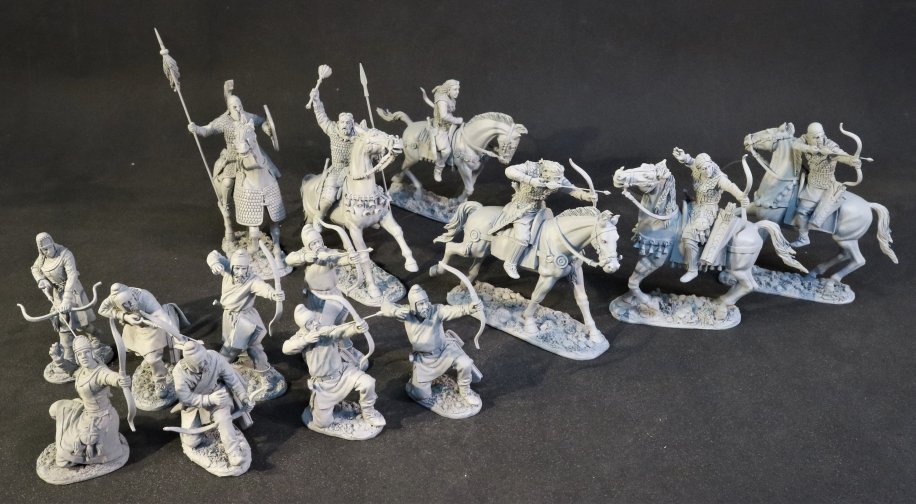
SY-16A
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF ANCIENT GREECE AND MACEDONIA,
THE SCYTHIANS,
SCYTHIAN FOOT ARCHERS.
(2 pcs)
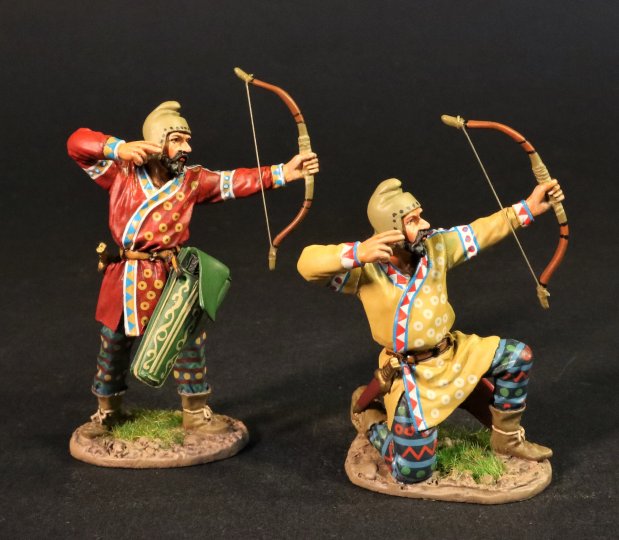

SY-16B
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF ANCIENT GREECE AND MACEDONIA,
THE SCYTHIANS,
SCYTHIAN FOOT ARCHERS.
(2 pcs)
In the aftermath of their defeat of the Persian invasion, Scythian power grew considerably, and they were to launch campaigns against their Thracian neighbours.
The Greek cities of the Northwestern Black Sea coast and parts of the Crimea were also invaded and were largely unsuccessful, as the Greeks united under the leadership of the city of Panticapaeum and put up a vigorous defence.
The 4[SUP]th[/SUP] century BC was a flowering of Scythian culture. The Scythian King Ateas managed to unite under his power the Scythian tribes. He was to conquer territories along the Danube as far as the Sava river and established a trade route from the Black Sea to the Adriatic.
The scythians apparently obtained most of their wealth from their control over the slave trade, but their trade routes were instrumental in opening up the silk road trade
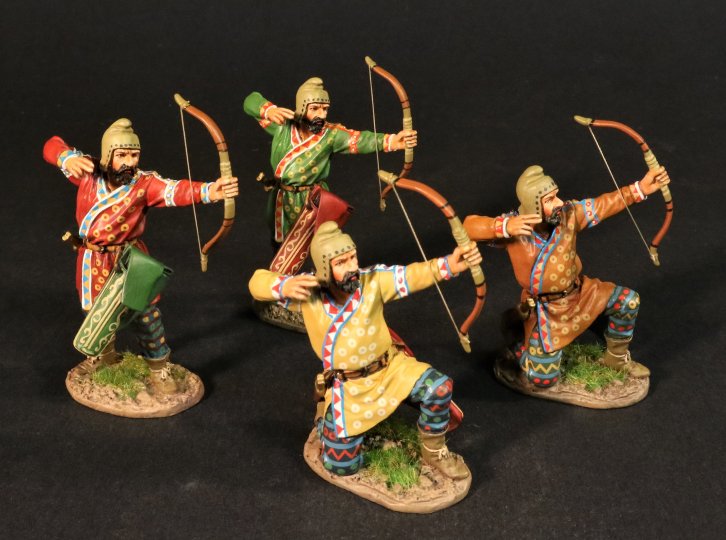

SY-16N
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF ANCIENT GREECE AND MACEDONIA,
THE SCYTHIANS,
SCYTHIAN FOOT ARCHERS.
(4 pcs)
The westward expansion of Ateas brought him into conflict with Philip II of Macedon, who took military action against the Scythians killing Ateas in battle.
Philip’s son Alexander the Great continued the conflict with the scythinas, and in 331BC his general Zopyrion invaded Scythian territory with a force of 30,000 men, but was routed and killed by the scythians near Olbia.
In the aftermath of conflict between Macedon and the Scythians, the Celts seem to have displaced the Scythians from the Balkans, whilst in south Russia, a kindred tribe, the Sarmatians, gradually overwhelmed them.
**PLEASE CONTACT YOUR LOCAL DEALER FOR FURTHER INFORMATION**
THE ANCIENTS COLLECTION
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF ANCIENT ROME
THE CARTHAGINIANS
Ancient Carthage was a Phoenician state founded in 814BC. The Carthaginian Empire was to extend over much of the coast of Northwest Africa as well as substantial parts of coastal Iberia and the islands of the western Mediterranean sea.
At its height, the city state served as a major hub of trade, which brought it into conflict with the Greeks in Sicily, and with the Roman Republic, which led to a series of conflicts known as the Punic Wars.
CARTHAGINIAN WARSHIP

BTCT-06
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF ANCIENT ROME,
THE CARTHAGINIANS,
CARTHAGINIAN OFFICER.
(1 pc)


BTCT-07
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF ANCIENT ROME,
THE CARTHAGINIANS,
CARTHAGINIAN STANDARD BEARER.
(1 pc)

The military of Carthage was one of the largest military forces in the ancient world. Although the navy was always Carthage’s main force, the army acquired a key role in the spread of Carthaginian power.
With its Phoenician origins, Carthage already had a long history as a seafaring people. This was helped in that the navy was a permanently manned force, whilst the army would be enlisted only for a particular campaign and then demobilized.
Therefore it was easier to understand how the Carthaginian army was a Combined arms force, which comprised light and heavy infantry, skirmishers, light and heavy cavalry, as well as elephants.
The supreme command of the military was initially held by the civilian “Suffetes” until the third century. Thereafter, professional military generals were appointed directly by the Carthaginian Senate.
Whilst the navy was mainly manned by citizens, the army was composed almost exclusively of foreign mercenary units, particularly Libyans, Numidians, Iberians, Gauls and Greeks.
Only when the city of Carthage itself was threatened would citizens be conscripted into infantry service.

BTCT-12
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF ANCIENT ROME,
THE CARTHAGINIANS,
SCORPION.
(1 pc)
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF GREECE AND MACEDONIA
THE SCYTHIANS
The Scythians were an ancient nomadic people living primarily in the region known as Scythia, which today comprises the Eurasian steppes of Kazakhstan, the Russian Steppes of the Siberian, Ural, Volga and Southern regions , and eastern Ukraine.

The Scythians were a warlike people. When engaged at war, almost the entire adult population including a large number of women, participated in battles. The Athenian historian Thucydides noted that no people in either Europe or Asia could resist the Scythians without outside aid.
The scythians were particularly known for their equestrian skills, and their use of the composite bow shot from horseback. With great mobility, the Scythians could absorb the attacks of more cumbersome foot and cavalry, just retreating into the steppes. Such tactics wore down their enemies, making them easier to defeat.
Due to their notorious reputation as aggressive warriors they frequently gained employment as mercenaries.
By the late 6[SUP]th[/SUP] Century BC, the Persian Achaemenid King Darius The Great had built Persia into becoming the most powerful empire in the world, stretching from Egypt to India.
Planning an invasion of Greece, Darius first sought to secure his northern flank against the Scythians.
Darius sent a fleet of over 600 ships into Scythian territory. The army captured several Scythian Nobles. The army according to Herodotus numbered 700,000 men.
Unable to withstand the direct force of the Persian army, the Scythians adopted a scorched earth strategy, while simultaneously harassing the extensive Persian supply lines. The Persians suffered heavy losses and only proceeded as far as the Sea of Azov.
Darius and his army eventually retreated across the Danube back into Persia, and the Scythians thereafter earned a reputation of invincibility among its neighboring peoples.

SY-16A
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF ANCIENT GREECE AND MACEDONIA,
THE SCYTHIANS,
SCYTHIAN FOOT ARCHERS.
(2 pcs)

SY-16B
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF ANCIENT GREECE AND MACEDONIA,
THE SCYTHIANS,
SCYTHIAN FOOT ARCHERS.
(2 pcs)
In the aftermath of their defeat of the Persian invasion, Scythian power grew considerably, and they were to launch campaigns against their Thracian neighbours.
The Greek cities of the Northwestern Black Sea coast and parts of the Crimea were also invaded and were largely unsuccessful, as the Greeks united under the leadership of the city of Panticapaeum and put up a vigorous defence.
The 4[SUP]th[/SUP] century BC was a flowering of Scythian culture. The Scythian King Ateas managed to unite under his power the Scythian tribes. He was to conquer territories along the Danube as far as the Sava river and established a trade route from the Black Sea to the Adriatic.
The scythians apparently obtained most of their wealth from their control over the slave trade, but their trade routes were instrumental in opening up the silk road trade

SY-16N
ARMIES AND ENEMIES OF ANCIENT GREECE AND MACEDONIA,
THE SCYTHIANS,
SCYTHIAN FOOT ARCHERS.
(4 pcs)
The westward expansion of Ateas brought him into conflict with Philip II of Macedon, who took military action against the Scythians killing Ateas in battle.
Philip’s son Alexander the Great continued the conflict with the scythinas, and in 331BC his general Zopyrion invaded Scythian territory with a force of 30,000 men, but was routed and killed by the scythians near Olbia.
In the aftermath of conflict between Macedon and the Scythians, the Celts seem to have displaced the Scythians from the Balkans, whilst in south Russia, a kindred tribe, the Sarmatians, gradually overwhelmed them.
**PLEASE CONTACT YOUR LOCAL DEALER FOR FURTHER INFORMATION**

